Immunotherapy biomarkers test
Immunotherapy biomarkers test
Biomarkers for immunotherapy
Modified from-The role of biomarkers in personalized immunotherapy.
By Sankar et. al. 2022, https://biomarkerres.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s40364-022-00378-0
Our comprehensive Cancer Panel provides a highly multiplexed target selection of genes implicated in cancer research. Encompassing over 50% of the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute Cancer Gene Census, this is the most comprehensive cancer gene panel available. With all-exon coverage of 409 genes, the GTA, and GTC Comprehensive Cancer Panels deliver fast, FFPE-compatible, target selection for a broad survey of key genes for semiconductor sequencing. The outstanding performance of our platform, utilizing only 10 ng of input DNA per primer pool for a total of 40 ng of input DNA, analysis of restricted samples like FFPE samples is possible.
The current FDA approved tissue biomarkers for solid malignancies including PD-L1, tumor mutational burden (TMB), and microsatellite instability (MSI).
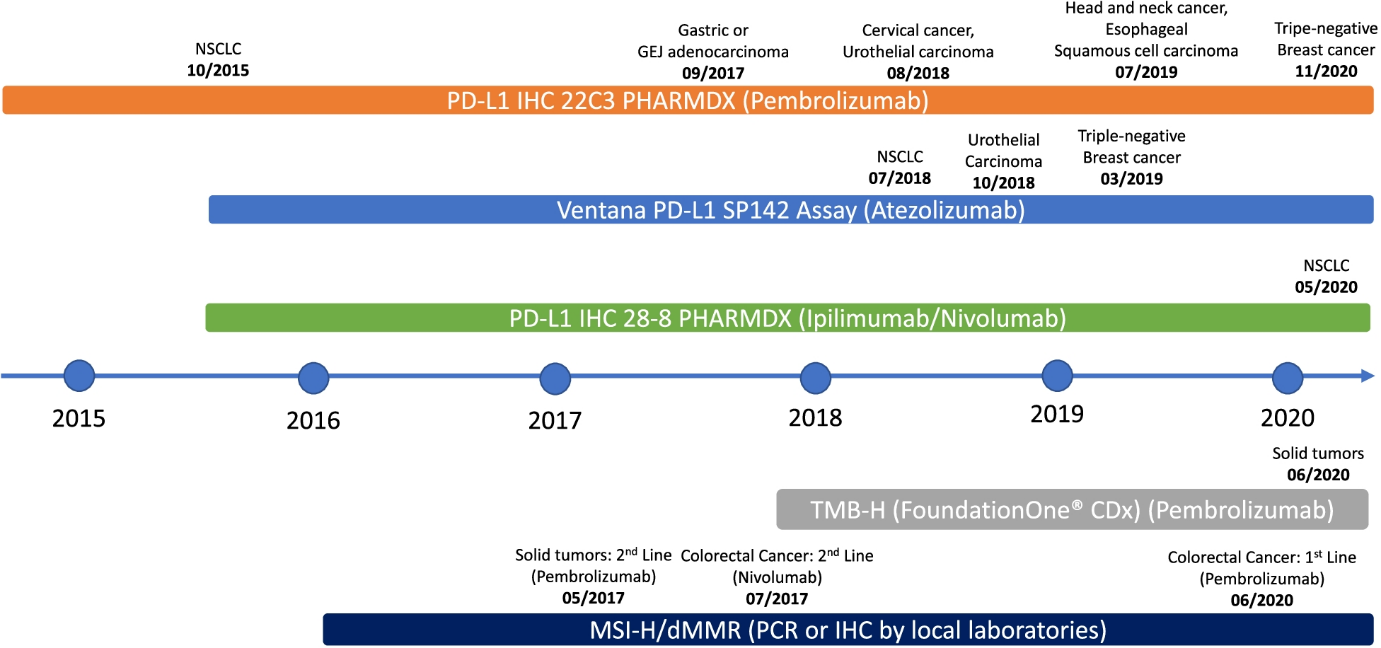
PD-L1
PD1 is expressed on activated tumor infiltrated lymphocytes (TILs) in various tumors, while PD ligands (PD-L1 and PD-L2) are commonly upregulated on tumor cell surfaces. PD-L1 expression on tumor cells or TILs determined by IHC has become a commonly used biomarker for selecting patients for ICI therapy across tumor types. PD-L1 IHC 22C3 pharmDx, PD-L1 IHC 28–8 pharmDx, and VENTANA PD-L1 (SP142) showed high concordance among pathologists for determination of PD-L1 expression on tumor cells; concordance of PD-L1 expression on immune cells was also demonstrated, albeit with greater variability. The two methods to score PD-L1 expression using the PD-L1 IHC 22C3 or 28–8 pharmDx assay are measurement of tumor proportion score (TPS) and combined positive score (CPS). PD-L1 expression on tumor cells assessed via TPS is a well validated biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The CPS method was developed to aid in selection of patients with urothelial cancer, gastric/gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma, triple-negative breast cancer, and ovarian cancer who would benefit from pembrolizumab. The VENTANA SP142 assay, on the other hand, uses the percentage of PD-L1 positive immune cells to determine PD-L1 expression on TILs: IC0 (< 1%), IC1 (≥ 1% but < 5%), and IC2/3 (≥ 5%).
It is important to note that PD-L1 is an imperfect biomarker by itself, as its expression can be triggered by active immune response (i.e., patients with a negative baseline PD-L1 stain might still respond to ICI). Further, tumors with high PD-L1 expression may be resistant to treatment. In fact, a study of 45 FDA approvals of ICI from 2011 to 2019 showed that PD-L1 was only predictive in 28.9% of cases and was either not predictive (53.3%) or not tested (17.8%) in the remaining cases. Only 9 of the approvals were linked to a specific PD-L1 threshold and companion diagnostic assay, with variable thresholds both within and across tumor types using several different assays, suggesting that PD-L1 testing has certain limitations which must be considered in clinical decision making. Therefore, various biomarkers predictive of ICI efficacy independent of PD-L1 status are being evaluated, many of which are described below.
MSI and TMB
MSI results from a defective DNA mismatch repair (dMMR) system which leads to clusters of thousands of mutations along microsatellite regions. Tumors with deficient MMR (dMMR) or high MSI (MSI-H) have increased mutational burden which leads to infiltration of T cells in the TME, leading to improved response with anti-PD1/PD-L1 therapies [16]. Furthermore, a higher TMB correlates with a greater probability of displaying neoantigens on the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) molecules of tumor cell surface, eliciting CD8+ T cell dependent immune responses and tumor cell lysis. Importantly, TMB as a continuous variable does not have a linear correlation with OS, whereas PD-L1 expression has correlated with OS in advanced NSCLC patients. MSI or MMR is tested using multiplex immunohistochemistry or molecular-based tests including polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and next-generation sequencing (NGS). TMB can be evaluated by whole exome sequencing (WES) or NGS gene panel assays, both of which have been used in clinical trials to correlate with response to ICI in melanoma, NSCLC, urothelial carcinoma, and colorectal cancer. In a pooled analysis of patients with various cancers treated with anti-PD1/PD-L1 therapies, patients with high TMB had significantly improved progression-free survival as compared to patients with low TMB.
In 2017, the U.S. FDA granted its first tissue/site-agnostic approval to pembrolizumab for patients with advanced cancers harboring MSI-H/dMMR who have progressed on prior therapies with no further satisfactory treatment options. Pembrolizumab has recently been approved in the first-line setting for patients with unresectable or metastatic MSI-H or dMMR colorectal cancer and for adult and pediatric patients with unresectable or metastatic TMB-H (≥ 10 mutations/megabase) solid tumors who have progressed on prior therapies with no acceptable alternatives.
07 September 2022
Viewed 614 times











